

 DIN EN ISO 15106-3 Part 3 - Film and sheeting: Measuring the water vapour transmission rate using the
DIN EN ISO 15106-3 Part 3 - Film and sheeting: Measuring the water vapour transmission rate using the
Water Vapour Transmission Rate (WVTR or MVTR) is the rate at which water flows through a sample per unit time. For this standard the sample is a plastic film or sheet. The measurement is taken at a specified temperature and vapour (partial) pressure. WVTR is commonly stated in different units (see our Conversion Units table
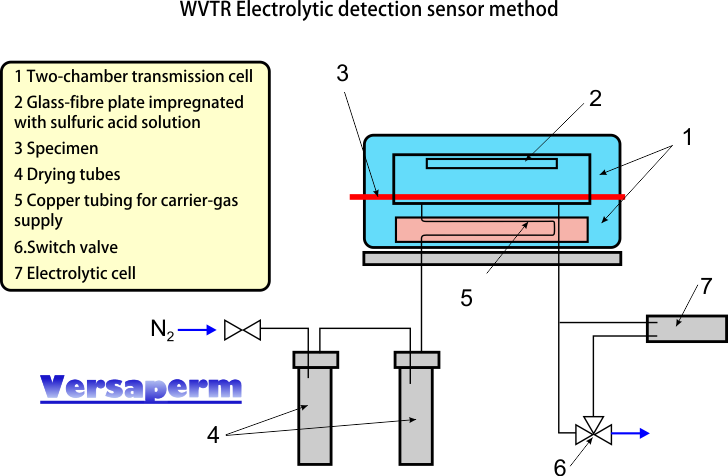
The gas transmission cell is split into two chambers by the film or sheet to be measured. One chamber is “dry” and the other has its humidity precisely controlled.
The dry side of the specimen is swept through by a dry carrier gas carrying any permeated water vapour permeating to an electrolytic cell for measurement. The cell includes two spiral wire electrodes, with a thin layer of phosphorous pentoxide coating mounted inside a glass capillary.
As the carrier gas flows through the glass capillary the moisture it holds is absorbed decomposed electrolytically into hydrogen and oxygen.
The mass of the moisture which permeate through the sample per unit time is calculated from the electrolytic current.
WVTR is critically dependent on temperature and relative humidity (partial pressure) and these must be stated. Care must also be taken to ensure that sample is wrinkles with no slackness.
The WVTR is critically dependent on temperature and relative humidity ( partial pressure) and these must be recorded. Care must also be taken to ensure there are no wrinkles or slackness in the specimen/.
Calculate the water vapour transmission rate of each test specimen using the following equation: